Epitalon (Epithalon)
$110 – $340
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic derivative of Epithalamin and a potential modulator of telomerase, the enzyme that maintains and protects the telomere caps at the ends of chromosomes (strands of DNA). Research suggests that Epithalon induces telomere elongation and may fight off the effects of aging as a result.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
What Is Epitalon (Epithalon)?
Epithalon (also known as Epitalon, Epithalone or Epithalamin) is a short synthetic peptide known to activate the telomerase enzyme and stimulate melatonin release. First developed in Russia in the 1980s, epithalon has been shown to delay age-related changes in reproductive and immune systems and increase the life span of mice and rats. Though it is primarily of interest in anti-aging research, epithalon has shown significant effects in certain types of cancer, infectious disease, and in DNA regulation.
Epitalon (Epithalon) Structure
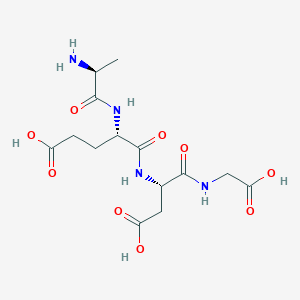
Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Molecular Weight: 390.349 g/mol
PubChem CID: 219042
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
Epitalon (Epithalon) Research
1. The Role of Telomerase in the Anti-Aging Effects of Epithalon
Early research using insects and rodents revealed that epithalon can prolong life substantially. In normal, healthy fruit flies and rats, epithalon decreases mortality by 52%. In mice prone to both heart disease and cancer, epithalon prolongs life by as much as 27% compared to controls. At least part of the answer to how epithalon achieves these profound effects is via its elimination of free radicals (charged molecules that do damage to healthy tissue).
Anti-oxidant activity is not the only reason that epithalon extends life, however. There is good evidence from in vitro experiments on human somatic cells to show that epithalon activates an enzyme called telomerase. Telomerase protects telomeres, the ends of chromosomes that are critical to ensuring the health of DNA. Epithalon’s activation of telomerase leads directly to a decrease in how many errors a strand of DNA contains, supporting the notion that epithalon protects DNA from damage. In short, epithalon protects DNA from accumulating errors over time, a process that eventually leads to cell dysfunction, aging, and even cancer in some cases.
2. Epitalon and DNA Activation
Neither its impact on free radicals nor its effects on telomeres seem sufficient to explain the profound effects that Epitalon has on longevity. Indeed, scientists are working hard to understand how this short peptide achieves the effects that it does so that the mechanisms can be explored in depth. As it turns out, at least part of the answer may come from the fact that epithalon changes the expression of certain genes.
Research in cell cultures shows that Epitalon interacts directly with DNA to turn on and enhance the expression of certain genes. Epitalon interacts with the promoter regions of genes for CD5, IL-2, MMP2, and Tram1. CD5 and IL-2 both affect the function of the immune system while MMP2 plays a critical role in the maintenance of extracellular matrix in skin, tendons, and other connective tissue. These findings suggest that epithalon may impact the function of the immune system and the ability of the body to heal itself following not only injury, but following typical day-to-day stress as well.
It is not surprising that Epitalon impacts the immune system. Research in rats indicates that Epitalon boost the expression of interferon gamma in aging lymphocytes. Interferon gamma is a critical signaling molecule in the immune system. It is important for fighting off viral infections through the activation of macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells.
The following are known DNA interactions of Epitalon:
- CD5 – Leads to immune cell differentiation.
- IL-2 – Increases IL-2 production, which regulates white blood cells.
- MMP2 – Enhances MMP activation and decreases inflammation.
- Tram1 – Enhances protein production.
- Arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase – Enhances melatonin production.
- pCREB t – Circadian rhythm regulation and anti-neoplastic effects.
- Telomerase – Telomerase activity increases cell longevity.
3. Epitalon and Skin Health
As stated above, Epitalon has a positive effect on the gene that regulates MMP2. MMP2 is a protein found in connective tissue like skin. Research in rodents indicates that not only does Epitalon activate this gene, it activates fibroblasts, the cells that produce and maintain MMP2 as well as other components of the extracellular matrix like collagen and elastin. Mice exposed to Epitalon show an increase in fibroblast activation of 30-45%. By activating fibroblasts, epithalon can help to boost rates of healing and offset the natural decline in skin structure and integrity that occurs with aging.
Further evidence for epithalon’s benefit in skin comes from the fact that it decreases caspase-3 activity. Caspase-3 is an enzyme in the apoptosis or programmed cell death pathway. By decreasing caspase-3 activity, epithalon helps to protect fibroblasts and other skin cells, keeping them alive and healthy for longer periods of time
4. Epithalon and Tumor Growth
Daily administration of epithalon to rats with cancer has been found to decrease tumor growth. Not only does the peptide reduce tumor growth, it prevents the metastasis or spread of these tumors to distant tissues as well. Epithalon is currently being investigated as a potential treatment for Her-2/neu positive breast cancers and is of interest in preventing the development of certain types of leukemia as well as testicular cancer.
There is some evidence that epithalon activates the gene for PER1 protein, which is found in the hypothalamus. PER1, which helps to regulate circadian rhythm, is under-expressed in cancer patients. It is unclear if this under-expression precedes cancer development and therefore contributes to cancer growth or is a consequence of cancer development. It is clear that the protein affects cancer growth once the cancer is established. Control of PER1 expression may be one means of naturally slowing tumor growth. Research shows that PER1 expression sensitizes cells to the effects of radiation and may therefore help to decrease the doses of radiation needed to treat certain cancers, a fact that would not only offset immediate side effects, but reduce the occurrence of secondary tumors following high doses of radiation.
5. Epithalon and Melatonin Secretion
Melatonin, which is linked to sleep and aging, is produced by the pineal gland. Research in rats shows that epithalon and similar peptides affect both the synthesis and release of melatonin by affecting the expression of two proteins (arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) and pCREB transcription protein).Both of these genes play an important role in melatonin production and in the circadian (day/night) control of melatonin release. Research in monkeys indicates that epithalon restores melatonin secretion to normal.
6. Epitalon and Eyesight
A trial in rats suffering from retinitis pigmentosa found that epithalon improves outcomes in 90% of patients. It appears that the peptide helps to preserver normal structure of the eye while boosting the bioelectric function of the retina necessary for vision.
| Dosage | 500mg (50mg x 10 Vials), 100mg (10mg x 10 Vials) |
|---|
Related Products
ACE-031 is a synthetic protein made up of activin receptor type IIB and the immunoglobulin G1-Fc (IgG1-Fc). It binds to myostatin and related proteins within muscle, rendering them inactive. Research shows it to be useful in stabilizing muscle mass and strength in both primary muscle-wasting disorders and neuromuscular conditions
10mg Kit
1mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Available on backorder
Melanotan 2 (MT-2) is a synthetic analogue of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Developed in the 1980s, Melanotan 2 has been shown to increase sexual arousal, reduce compulsive/addictive behavior, curb hunger, and promote lean body mass. Research has shown the peptide to stimulate melanocytes therefore producing increased skin pigmentation and may help to combat autism when used during early childhood development.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Hexarelin is a synthetic analogue of ghrelin that shows benefit in heart disease and cardiac ischemia, protecting the heart following heart attack. Research has shown that Hexarelin also protects skeletal muscle against wasting and improves cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
10mg Kit
1mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
AOD-9604 is a modified version of the hGH fragment 176-191 peptide (contains a di-sulfide bridge) and thus a derivative of human growth hormone (hGH). Originally developed as a lipolytic (fat burning) compound, AOD9604 has shown benefit in studies of heart disease, osteoarthritis/cartilage repair, and metabolic syndrome. AOD9604 stimulates lipolysis (the breakdown or destruction of fat) and inhibits lipogenesis in animal studies.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Gonadorelin is a gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist that has shown benefit in the treatment of infertility and hypogonadism. Recent research suggests that gonadorelin may be useful in slowing the growth of breast and prostate cancer. Studies also show promise in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
20mg Kit
2mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
IGF-1 DES is a truncated, natural version (splice variant) of insulin-like growth factor-1. Naturally found in the brain, breast milk, and uterine tissue, IGF-1 DES stimulates hypertrophy and hyperplasia of a number of different cell lines. Research has shown this version of the protein to be more potent than standard IGF-1, mostly as a result of its enhanced bioavailability. Currently, researchers are looking at ways to utilize IGF-1 DES in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), autism, and a variety of neurological conditions. Research shows that it helps to maintain the health of synaptic connections in the central nervous system and, like all IGF-1, promotes the repair of muscle and connective tissue.
10mg Kit
1mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Oxytocin, a natural protein hormone, plays important roles in sexual reproduction, childbirth, bonding between mother and child during breast feeding and wound healing. New research suggests that it may boost cognitive performance, reduce cardiovascular risk, and offset the effects of diabetes.
20mg Kit
2mg x 10 vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
GHRP-6 is a synthetic ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue agonist. It has positive effects on appetite, heart muscle cells, scar formation, and sexual motivation. Animal studies show this orally active growth hormone secretagogue also improves memory function and may help to thwart the neurological effects of Parkinson’s disease.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Categories
Tags
- 100iu
- Anastrazole
- anti aging
- anti wrinkles
- Arimidex
- Bodybuilding
- cjc
- cjc1295
- cjc 1295
- Clomid
- cycle
- dianbol
- fat loss
- genotropin
- gh
- ghrp
- gnrh
- growth hormone
- hgh
- human growth
- human growth hormone
- hygetropin
- igf
- igf-1
- jenotropin
- kingotropin
- kit
- methanabol
- methandione
- mgf
- nordictropin
- norditropin
- orals
- pct
- peptide
- peptides
- primo
- Primobolan
- roid
- roids
- Sarms
- somatropin
- steroid
- steroids
- testosterone