Description
KPV is a potent anti-inflammatory peptide that has shown promise in a number of disease conditions. The most active research is in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease where the peptide has showed substantial promise. KPV has been shown in animal studies to be safe and effective when administered orally, intravenously, subcutaneously and transdermal. Research in wound healing also reveals that KPV and other alpha-MSH derivatives may offer a host of benefits that speed wound healing, reduce infection, fight inflammation, and lead to better cosmetic results. KPV and similar peptides could become mainstays not just in wound healing, but in scar reduction following surgery.
What is KPV?
KPV is the C-terminal peptide fragment of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH). It is one of many short peptide derivatives of alpha-MSH that has been tested to determine if they retain similar photoprotective properties, activity against ischemia, sexual effects, or benefits on feeding behavior and energy homeostasis. KPV, which is made up of lysine-proline-valine turns out to have significant anti-inflammatory effects. The peptide is under active research as a potential therapeutic in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. It has shown evidence of potent anti-inflammatory activity in the central nervous system, GI tract, lungs, vascular system, and joints. Because KPV is a small peptide, it can be administered in multiple ways including oral, intravenous, and transdermal routes.
Structure
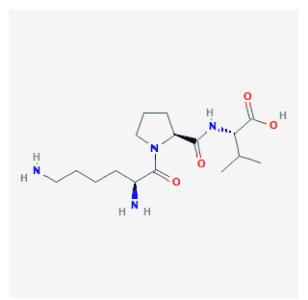
Source: PubChem
KPV Research
Intestinal Inflammation
Perhaps the most important discovery to arise from KPV research is the finding that the peptide reduces intestinal inflammation. In mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), KPV shows robust results, reducing inflammatory infiltrates, MPO activity, and overall histological evidence of inflammation. Mice treated with KPV in the study recovered faster and had more pronounced weight gain than mice treated with placebo.
Further research on delivery mechanisms for KPV has revealed that loading KPV onto nanoparticles functionalized with hyaluronic acid helps to direct the inflammatory effects of the peptide to proper locations within the intestine. This leads to accelerated mucosal healing and alleviation of inflammation via a strong down regulation of TNF-alpha in mouse models. In many ways, KPV is a more effective and more targeted means of reducing inflammation in IBD without affecting TNF-alpha in other locations in the body. The benefit of modifying KPV is in improving the peptide’s oral bioavailability. This does not increase the efficacy of the peptide, but does have an impact on potency and thus total dose require to achieve an effect.
Research suggests that TNF-alpha is not the only inflammatory mediator that KPV has an impact on. The peptide also reduces NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. These effects work in tandem with TNF-alpha inhibition to reduce inflammatory changes in the intestine. Mice treated with KPV have substantially less colonic infiltration and normal colon lengths compared to controls.
KPV as a General Anti-Inflammatory
As far back as 1984, research in rabbits revealed that KPV is a powerful anti-inflammatory and fever reducer (anti-pyretic). In this setting, however, KPV had lower potency than the full alpha-MSH molecule. This suggested to scientists at the time that KPV was lacking some portion of the alpha-MSH molecule necessary for full anti-pyretic activity. What ensued was decades of research investigating various modified forms of alpha-MSH.
Perhaps the biggest lesson learned from these tests is that alpha-MSH and several of its analogues all reduce inflammation in a wide variety of disease. So far, the molecules have been tested in fever, irritant and allergic contact dermatitis, vasculitis, fibrosis, arthritis and inflammation of the eyes, brain, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. In all cases, alpha-MSH is the most effective anti-inflammatory. Unfortunately, it suffers from one major side effect – it causes skin pigmentation. KPV, on the other hand, does not have this side effect. And even though KPV is not as potent as the intact alpha-MSH, its lack of side effects means that boosting levels to achieve desired target effects is theoretically possible in most cases.
The difference in potency has been found to be minimal, at best, as the majority of anti-inflammatory effects of alpha-MSH are, in fact, due to the KPV section. What is interesting, however, is that the parent molecule appears to be better at suppressing late-stage inflammatory reaction. In the case of contact dermatitis, for instance, alpha-MSH does a better job of preventing an allergic inflammatory response at 2 weeks post initial exposure. This suggests that alpha-MSH may be affecting some aspect of immune modulation that is separate from the immediate inflammatory response. Work is still being done to determine what this process is.
Wound Healing
Wound healing is a complex physiological process. Scientists have identified three general phases in the wound healing process: inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling. Each phase is characterized by differences in cell populations and cytokine concentrations and represents a unique chemical/physiological milieu for potential intervention. Research shows that even though each stage of the wound healing process is characterized by different skin cell subtypes, the majority of these cells express a melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) that binds alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Of course, this also means that these cell types bind alpha-MSH analogues like KPV and KdPT as well.
Because these alpha-MSH derivatives retain some of the properties of alpha-MSH, but lack others, they offer potential benefits in wound healing. For instance, KPV offers the inflammatory properties of alpha-MSH, but lacks the pigment-inducing activity of its parent peptide. This makes it a good candidate for improving wound healing while avoiding the skin-changing characteristics often associated with natural scar formation (a phenomenon disproportionately affecting darker-skinned individuals).
One of the reasons that KPV is anti-inflammatory is that it participates in the innate immune response against two common skin pathogens. Research shows that KPV inhibits the growth of both Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans. These benefits occur at physiological concentrations, meaning that KPV could provide an effective means of preventing infection in the setting of serious wounds like burns. This benefit of KPV is in contrast to other anti-inflammatory medications that actually inhibit the ability of the body to fight off infection. Thus, KPV combines anti-inflammatory activity with antimicrobial activity.
Scar Formation
In accordance with the known benefits of KPV in first stage (inflammation) of wound healing, research has also investigated its role in the other two stages of wound healing. It appears that this peptide is able to reduce the kind of chronic inflammation that leads to hypertrophic scar (e.g., keloid) formation. This type of scarring is characterized by widespread macrophage infiltration, TNF immunoreactivity, and neutrophil abundance. Administration of alpha-MSH in this setting leads to smaller scars and a less drastic inflammatory response. Similar effects have been noted in other tissues such as lung and heart. These findings raise the hope that KPV could be useful in preventing the kind of scarring seen with certain chemotherapy agents. This would not only reduce the side effects of cancer treatment, but could allow for the use of increased concentrations of these medications and thus better outcomes in cancer treatment.
According to Dr. Didier Merlin, at least part of the benefit of KPV in reducing scar prominence appears to arise from its ability to modulate collagen metabolism. Alpha-MSH and its analogues suppress IL-8 secretion, which inhibits collagen type 1 production. This is important during the last phase of wound healing, remodeling, as it has been shown that people prone to keloid formation and hypertrophic scarring have less MC1R mRNA expression on dermal fibroblasts.
KPV Summary
KPV is a potent anti-inflammatory peptide that has shown promise in a number of disease conditions. The most active research is in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease where the peptide has showed substantial promise. KPV has been shown in animal studies to be safe and effective when administered orally, intravenously, subcutaneously and through the skin. Research in wound healing also reveals that KPV and other alpha-MSH derivatives may offer a host of benefits that speed wound healing, reduce infection, fight inflammation, and lead to better cosmetic results.