GHK-Cu (Copper Peptide)
$99 – $149
The human peptide GHK-CU Copper Peptide (glycyl-l-histidyl-l-lysine) has multiple biological actions, all of which, according to our current knowledge, appear to be health positive. It stimulates blood vessel and nerve outgrowth, increases collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycan synthesis, as well as supports the function of dermal fibroblasts and anti-aging.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
GHK (GHK-CU) Copper Peptide
GHK-Cu, Copper Peptide, is a naturally occurring human Tri-Peptide. In plasma, the level of GHK-Cu is about 200 ng/ml at age 20. By the age of 60, the level drops to 80 ng/ml. Scientific studies conducted in different research laboratories around the world have established that human Tri-Peptide GHK-Cu possesses a Plethora of biological actions including activation of wound healing, attraction of immune cells, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory effects, stimulation of Collagen and Glycosaminoglycan Synthesis in Skin Fibroblasts and promotion of blood vessels growth. Recent studies indicate its important role in Stem Cell Biology and Anti-Tumor defense. Since GHK-Cu plays an important role in Skin Biology, it is widely used in cosmetics as a reparative and Anti-Aging ingredient. The levels of GHK decrease as you age.
GHK-CU Structure
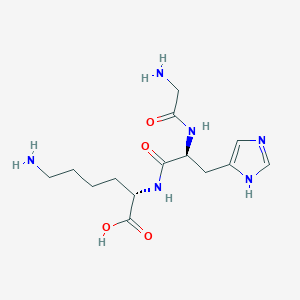
Source: PubChem
Sequence: Gly-His-Lys.Cu.xHAc
Molecular Weight: 340.384 g/mol
PubChem CID: 73587
CAS Number: 89030-95-5
GHK-CU Human Trials
A 2% GHK gel showed promising results in treatment of 120 Diabetic patients, increasing the percentage of ulcer closure from 60.8% to 98.5%, and decreasing the percentage of infection from 34% to 7%.
Cosmetics Use:
GHK-Cu is widely used in Anti-Aging cosmetics, several controlled facial studies confirmed the Anti-Aging, firming, and anti-wrinkle activity of copper peptide GHK-Cu.a study showed facial cream containing GHK-Cu increased collagen in photoaged skin of 20 female volunteers, performing better than vitamin C and retinoic acid. Leyden et al. conducted 12 weeks facial study of GHK-Cu containing face and eye cream, reporting significant improvement of skin laxity, clarity and appearance, reduced fine lines and the depths of wrinkles, and increased skin density and thickness compared to placebo. GHK-Cu eye cream performed better than vitamin K cream. Finkley et al. conducted a 12-week facial study on 67 women and reported that GHK-Cu cream applied twice daily improved aged skin appearance, increased thickness, reduced wrinkles, and strongly stimulated dermal keratinocyte proliferation as determined by histological analysis of biopsies. The same study found copper peptide GHK-Cu to be non-toxic and non-irritating.
Hair Growth Benefits
Copper peptide GHK and its analogues were found to strongly stimulate hair growth. The efficiency of synthetic analog of GHK-Cu was similar to that of 5% minoxidil.
Skin Healing
GHK-Cu is a natural part of human blood and, as such, has been found to play an integral role in skin regeneration pathways and Anti-Aging. Research in skin cultures has found that GHK stimulates the synthesis and breakdown of collagen, glycosaminoglycans, and other extracellular matrix components like proteoglycans and chondroitin sulfate which helps in anti-aging. At least part of this effect is mediated through the positive recruitment benefits that GHK-Cu has on fibroblasts, immune cells, and endothelial cells. The peptide draws these cells to the site of injury and appears to coordinate their activity in repairing the damage.
GHK-Cu is a common component of skin-care and cosmetic products. It improves elasticity of the skin Anti-Aging while tightening and firming. It has also been shown to reduce damage due to sunlight, reduce hyperpigmentation, and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. The ability of GHK-Cu to modulate collagen synthesis is important in reducing the appearance of scars, preventing hypertrophic healing from taking place, smoothing rough skin, , and repair the structure of aged skin. These roles of GHK-Cu are mediated partly though its ability to boost levels of transforming growth factor-Β. It is likely that the peptide works through several different biochemical pathways and that it has effects and the level of gene transcription.
Research in mice shows that GHK-Cu increases the rate of healing following burn by as much as 33%. It appears that besides recruiting immune cells and fibroblasts to the site of injury, GHK-Cu also encourages the growth of blood vessels. Burned skin is often slow to regrow blood vessels due the cauterization effect, so these findings open up a new pathway for improving wound care in burn units and accelerating healing.
GHK-CU and Bacteria
The invasion of tissue by foreign pathogens is one of the primary reasons that wounds are slow to heal or do not heal at all. Bacterial and fungal infections are particularly problematic in burn patients and in those with compromised immune systems (e.g. diabetes, HIV). GHK-Cu, when combined with certain fatty acids, creates a potent antimicrobial compound that is active against a number of bacteria and fungi known to complicate wound healing.
Research in diabetic patients has shown that GHK-Cu is superior to standard care regimens alone in the treatment of diabetic ulcers. Patients given both standard care and GHK-Cu showed a ~40% increase in wound closure and a 27% decrease in rates of infection compared to control groups.
Cognition and Nervous System Function
The death of neurons due to degenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s is poorly understood. This makes it difficult to develop treatments and those that are available are generally of limited efficacy. Research, however, suggests that GHK-Cu can counter the age-associated decline in neuron function that often underlies these diseases. Research shows that GHK-Cu can improve angiogenesis in the nervous system, boost nerve outgrowth, and reduce inflammation in the central nervous system. There is even evidence that GHK-Cu can reset pathological gene expression and help to recreate a state of health in dysfunctional systems.
Brain contains a high concentration of GHK-CU, though levels of the peptide decline with age. There is a thought, among scientists, that GHK-Cu may protect nervous system tissues against natural insults such as gene dysregulation and that it is the decline in GHK-Cu with age, and not the onset of new disease processes, that actually leads to neurodegeneration.
Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Research in mice shows that GHK-Cu can protect the lungs against fibrosis that occurs following therapy with the cancer drug bleomycin. This could pave the way for using GHK-Cu as a chemotherapy adjuvant that allows doses of these life-saving medications to be increased without risk of increased side effects. The study when a step farther, than usual, by identifying the likely pathway by which GHKC-Cu protects against fibrosis. It appears that the peptide regulations TNF-alpha dn IL-6 levels, both of which act as inflammatory molecules and affect the extracellular matrix and smooth muscle of the lung. By reducing inflammation in the lungs, GHK-Cu prevents fibrotic remodeling from taking place and improves collagen deposition.
Similar benefit of GHK-Cu in protecting lungs was found in mouse models of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), an inflammatory lung condition that can develop rapidly and be fatal. ARDS is associated with injury, infection, and certain drugs like those used in chemotherapy. Once again, GHK-Cu appeared to mediate its effects through decreased TNF-alpha and IL-6 expression.
Pain Reduction
In rat models, the administration of GHK-Cu had a dose-dependent effect on pain-induced behavior. The peptide appears to have analgesic effects that are produced through increased levels of the natural painkiller L-lysine. Similar research has found that the peptide can also increase levels of L-arginine, another analgesic amino acid. These findings open up new avenues for pain control that do not rely on addictive opiate medications or NSAIDs, which have been found to have negative effects on the heart.
GHK-Cu exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. GHK-Cu for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy GHK-Cu if you are a licensed researcher.
Current Research:
Human FibroBlasts: Recent studies have revealed many new aspects of molecular actions of the copper-peptide GHK. Pollard, was able to restore the function of human fibroblasts damaged by radiation treatment thus accelerating the healing and regenerative processes.
Nerve Regeneration: GHK promotes nerve regeneration. Axon regeneration was studied using collagen tubes with incorporated peptides. GHK increased the production of nerve growth factors, and expression of integrins and increased the rate of regeneration of myelinated nerve fibers.
Stem Cells: In 2009, a group of researchers from the Seoul National University (Republic of Korea) demonstrated that the copper-peptide stimulated the proliferation of keratinocytes and increased the expression of integrins and p63 protein in the epidermal stem cells.
Since p63 is considered to be an important marker of stem cell and Anti-Senescence protein, the authors concluded that GHK-copper can revive the proliferative potential of epidermal stem cells and increase their ability to repair tissue.
Anti-Cancer Effects: In 2010, (the Department of Colorectal Surgery, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore) demonstrated that it can reverse the expression of certain genes involved in the metastatic spreading of colon cancer. it was effective at a very low concentration.
| Dosage | 1000mg (100mg X 10 Vials), 500mg (50mg x 10 Vials) |
|---|
Related Products
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Melanotan (MT-1) It is used clinically, to prevent sun-related skin damage (i.e. phototoxicity) from occurring in people suffering from erythropoietic protoporphyria. Though initially developed as a sunless tanning agent, melanotan 1 has been found to have a number of physiologic effects on blood pressure, feeding behavior, central nervous system function, and more.
100mg Kit
10mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Out of stock
Hexarelin is a synthetic analogue of ghrelin that shows benefit in heart disease and cardiac ischemia, protecting the heart following heart attack. Research has shown that Hexarelin also protects skeletal muscle against wasting and improves cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
10mg Kit
1mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Out of stock
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
ACE-031 is a synthetic protein made up of activin receptor type IIB and the immunoglobulin G1-Fc (IgG1-Fc). It binds to myostatin and related proteins within muscle, rendering them inactive. Research shows it to be useful in stabilizing muscle mass and strength in both primary muscle-wasting disorders and neuromuscular conditions
10mg Kit
1mg X 10 Vials
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Available on backorder
All Peptides are shipped non labeled
Categories
Tags
- 100iu
- Anastrazole
- anti aging
- anti wrinkles
- Arimidex
- Bodybuilding
- cjc
- cjc1295
- cjc 1295
- Clomid
- cycle
- dianbol
- fat loss
- genotropin
- gh
- ghrp
- gnrh
- growth hormone
- hgh
- human growth
- human growth hormone
- hygetropin
- igf
- igf-1
- jenotropin
- kingotropin
- kit
- methanabol
- methandione
- mgf
- nordictropin
- norditropin
- orals
- pct
- peptide
- peptides
- primo
- Primobolan
- roid
- roids
- Sarms
- somatropin
- steroid
- steroids
- testosterone