Description
NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is the naturally occurring oxidized form of NADH. Studies suggest its potential benefits include enhancing muscle function, protecting nervous system cells, and mitigating the effects of aging.
What Is NAD+
short for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is the oxidized form of NADH. It’s main biological function is to carry electrons from one biochemical reaction to another, acting to shuttle energy within a cell and, in certain conditions, to extracellular locations as well. NAD+ also plays roles in enzyme activation/deactivation, posttranslational modification of proteins, and cell-to-cell communication. As an extracellular signaling molecule, NAD+ has been found to be released from neurons in blood vessels, the bladder, the large intestine, and from certain neurons in the brain.
Structure
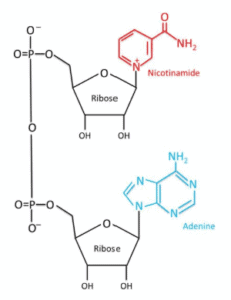
Source: PubMed
NAD+ Effects & Benefits
- NAD+ is best thought of as a support molecule that is essential to cellular metabolism as well as extracellular communication. Research shows an important role in energy conversion, DNA repair, immune defense, and circadian cycles. Levels of the cofactor, however, are sensitive to disease state as well as age. NAD+ as the following effects that decline as a result of natural age-related decreases in the levels of the cofactor.
- NAD+ activates sirtuins and other enzymes, liked Poly-ADP-ribose polymerases, involved in DNA repair and inflammatory processes. Sirtuins are the same enzymes linked to the life-extending benefits of calorie restriction.
- NAD+ controls the production of the protein PGC-1-alpha, which protects neurons and other cells in the central nervous system from oxidative stress. Research in mice shows that this particular effect may be linked to improved memory, particularly with aging.
- In mouse models, NAD+ helps to protect blood vessels against age-related hardening and the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques. In some studies, the cofactor even helps to reverse age-related dysfunction of the aorta.
- Mice given NAD+ show increased rates of metabolism and improved lean body mass.
- Increased levels can increase muscle strength and endurance in older mice.
- NAD+ has been linked to extracellular signaling, particularly for smooth muscle. It may be of benefit in GI function. This effect is likely responsible for NAD+ benefits on blood pressure>