Description
What Is FOXO4-D-Retro-Inverso (DRI)?
FOXO4 is a member of a larger group of genes that produce transcription factor Proteins essential in growth and differentiation. The FOXO4 protein is modified in normal biology by Post-translational activities. These modifications alter the DNA binding Affinity of FOXO4 and thus allow it to regulate a host of Cellular Pathways such as Oxidative stress signaling, Cellular Senescence, Apoptosis, insulin signaling, and the cell cycle itself. The FOXO4 protein is high in Placenta, ovaries, testes, fat cells, and adrenal glands.
FOXO4 D-Retro-Inverso is identical to the protein product of the FOXO4 gene, but the typical L amino acids have been exchanged for D amino acids. The result is that FOXO4-DRI has reduced susceptibility to standard Physiologic Clearance Mechanisms and thus remains in the body for extended periods. The modified protein is still capable of affecting transcription and Cellular Pathways. In general, the FOXO4-DRI protein interferes with normal FOXO4 function.
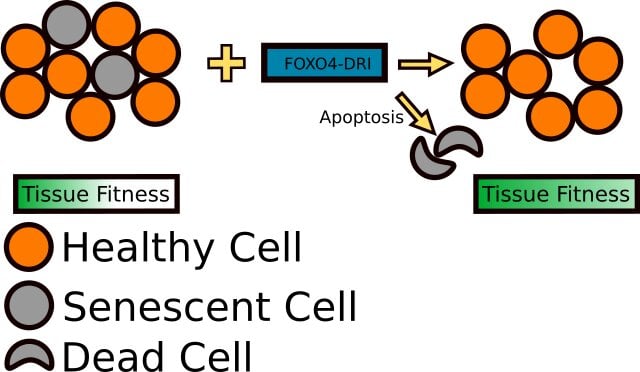
Of greatest interest in terms of aging and senescence is the ability of FOXO4-DRI to interfere with normal FOXO4 signaling in the cell cycle by preventing the binding of FOXO4 to p53. The p53 protein is an important regulator of progression through the cell cycle and programmed cell death (Apoptosis). When FOXO4-DRI binds to p53, it prevents FOXO4 from binding and allows p53 to bind to DNA allowing the cell to continue through the process of Apoptosis and die. Interestingly, FOXO4-DRI appears only to have this effect in senescent cells, cells that are no longer functional or dysfunctional due to aging. By targeting these Dysfunctional cells, FOXO4-DRI helps rid tissue of cells that are dead weight. So it allows for better tissue functioning and helps to stimulate the growth and differentiation of younger, healthier cells. The net result is a better Biological function and thus a decrease in “Biological age.”
“DRI” Retro Inverso Peptides Explained
DRI-Retro Inverso Peptides Explained Retro-Inverso Peptides are linear Peptides whose amino acid sequence is reversed, and the α-center chirality of the amino acid subunits is inverted as well. Usually, these Peptides are designed by including D-amino acids in the reverse sequence to help maintain side chain Topology similar to the original L-Amino Acid Peptide and make them more resistant to Proteolytic Degradation. Other reported synonyms for these Peptides in the scientific literature are Retro-Inverso Peptides, All-D-Retro Peptides, Retro-Enantio Peptides, Retro-Inverso Analogs, Retro-Inverso Analogues, Retro-Inverso Derivatives, and Retro-Inverso Isomers. D-amino acids represent conformational mirror images of natural L-amino acids occurring in natural Proteins in Biological systems. Peptides that contain D-amino acids have advantages over Peptides that contain L-amino acids. Generally, these Peptides are less susceptible to Proteolytic Degradation and have a longer adequate time when used in Pharmaceuticals.
Furthermore, inserting D-amino acids in sequence regions as sequence blocks containing only D-amino acids allows the design of Bioactive Peptide-based drugs that possess increased Bioavailability, in addition to being resistant to Proteolysis. Furthermore, Retro-Inverso Peptides can have binding characteristics similar to L-Peptides if adequately designed. Retro-Inverso Peptides are valuable candidates for the study of Protein-protein interactions by designing Peptidomimetics that mimic the shape of Peptide Epitopes, Protein-protein, or Protein-Peptide interfaces. Retro-Inverso-Peptides are attractive alternatives to L-Peptides used in Pharmaceuticals.
FOXO4-DRI Peptide Structure
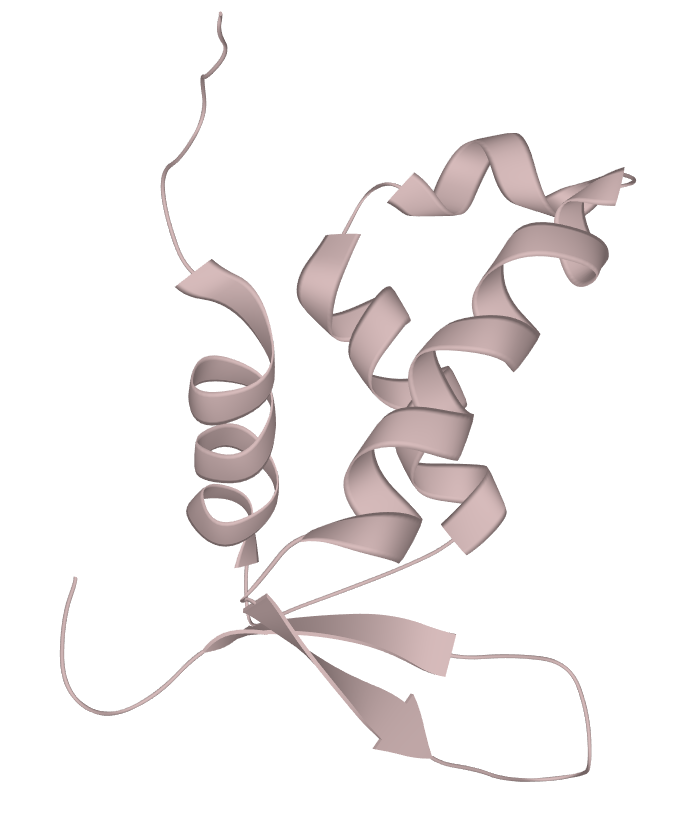 Source: Uniprot
Source: Uniprot
Sequence: H-D-Leu-D-Thr-D-Leu-D-Arg-D-Lys-D-Glu-D-Pro-D-Ala-D-Ser-D-Glu-D-Ile-D-Ala-D-Gln-D-Ser-D-Ile-D-Leu-D-Glu-D-Ala-D-Tyr-D-Ser-D-Gln-D-Asn-D-Gly-D-Trp-D-Ala-D-Asn-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Ser-D-Gly-D-Gly-D-Lys-D-Arg-D-Pro-D-Pro-D-Pro-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Gln-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Lys-D-Lys-D-Arg-D-Gly-OH
Molecular Formula: C228H388N86O64
Molecular Weight: 5358.05
Synonyms: Forkhead box protein O4, Proxofim, FOXO4a, AFX, AFX1, MLLT7
FOXO4-DRI Aging and Senescence
There is, however, good evidence that helps to elucidate the mechanisms by which the protein has its effects. Research in the well-studied nematode C. Elegans shows that FOXO4 affects insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling and, thus, cellular lifespan control, stress resistance, and gene regulation. It also appears that FOXO4 interacts with the p53 protein to regulate the cell cycle.
Natural FOXO4 protects senescent cells by keeping p53, a cell cycle regulator, sequestered and unable to induce Apoptosis. FOXO4-DRI disrupts the standard FOXO4/p53 mechanism and allows the latter protein to induce Apoptosis in senescent cells. The result is an Amelioration of senescence-associated loss of tissue homeostasis. Scientists refer to this as Rejuvenation by Therapeutic elimination of senescent cells. The process is similar to pruning a fruit tree. energy is redirected to healthier parts of the free by removing dead and damaged branches (Senescent cells). This same process happens at the organ and tissue level when cells contributing to overall unhealthy function are removed, allowing resources to be focused on healthy cells.
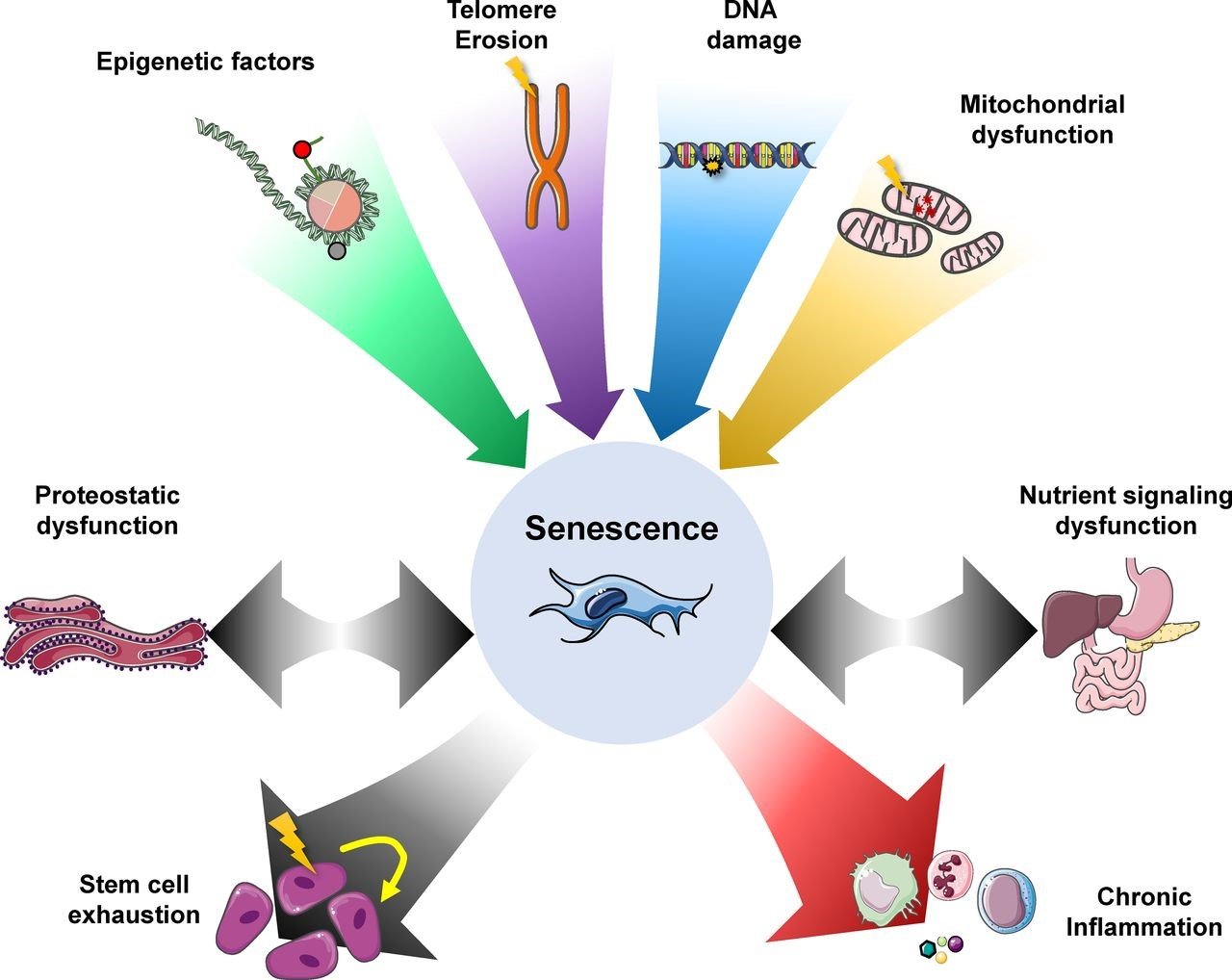 Source: Journal of Cell Biology
Source: Journal of Cell Biology
FOXO4-DRI Aging and Senescence
This image displays what factors contribute to senescence and what the outcomes are senescence are. Note that eliminating a senescent cell does not alleviate stem cell exhaustion but may slow it down. It does, however, help to reduce chronic Inflammation, a well-established driver of some conditions like cardiac disease, stroke, etc.
Irreparable damage, which is cellular damage beyond the body’s ability to fix, is one of the primary limitations to health span. Health span, the length of time an Organism remains healthy and functioning optimally, is generally shorter than Lifespan. A decline in Healthspan manifests as aging. The ability to extend our health span may not result in more years lived, but it can result in living out the years allotted to us in greater health and with better functioning. FOXO4 improves health span in aged mice, increasing fitness, fur density, and renal functioning. The mice do not necessarily live longer but have more significant health, even into old age. This translates into less disability and fewer Age-related conditions like heart disease, Musculoskeletal Dysfunction, etc.
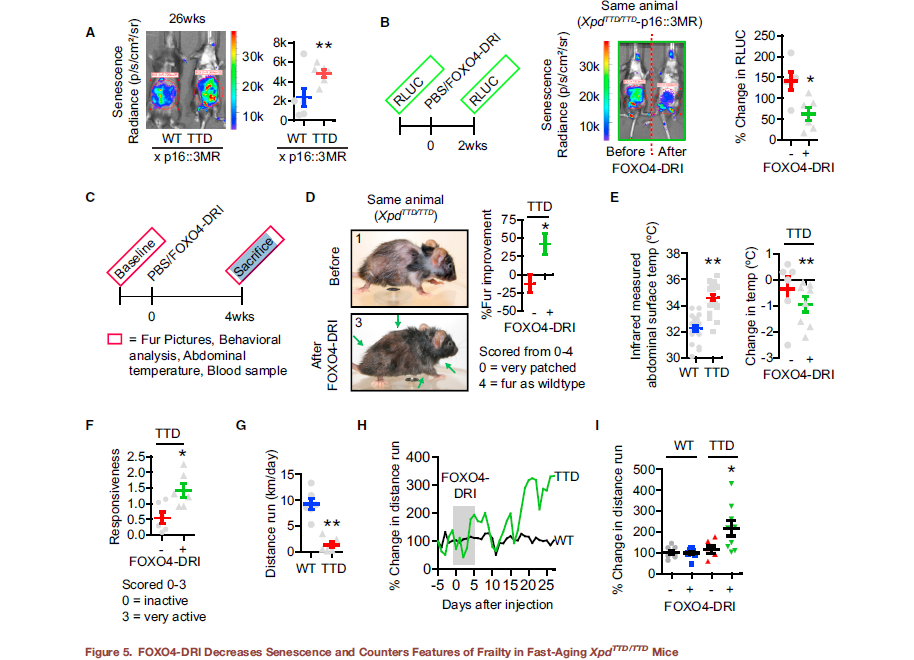
Images showing improved fitness, as shown by fur density, in a mouse treated with FOXO4-DRI after subjected to Chemotoxic agents used to model aging:
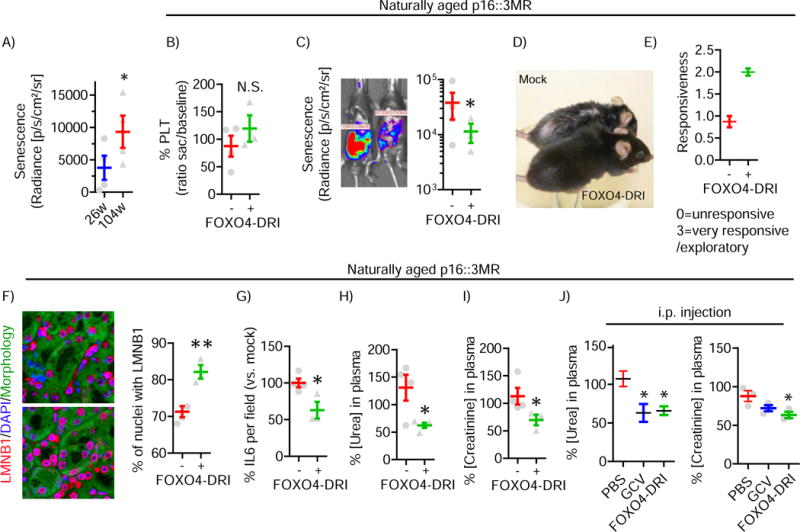
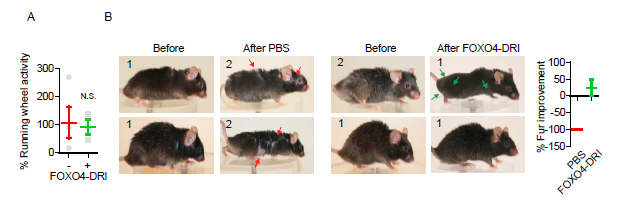
Source: Pubmed.
FOXO4-DRI Research
Insulin Signaling
FOXO Proteins are essential regulators of insulin signaling but act Downstream of the insulin itself and Insulin-like growth factors. Research in animal models indicates that FOXO mediates the Inhibitor effects of insulin and Insulin-like growth factor on cell Metabolism, growth, differentiation, Oxidative stress, and more. Mutations in FOXO are connected to pathologic changes in insulin signaling and the development of Metabolic disease and cancer. In people with Diabetes, alterations of FOXO signaling leads to fasting Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia. The latter is one of the most concerning aspects of Diabetes as it leads to many of the complications of the disease, such as kidney damage, stroke, heart attack, impaired wound healing, and more. The ability to regulate FOXO signaling in Diabetes could provide more targeted, more effective methods of preventing some of the severe complications of the disease. FOXO4-DRI effects the downstream of Insluin by reducing fasting blood sugar levels.
Heart Disease
Age is a risk factor for Cardiovascular disease, and declines in Proteasome activity in the heart mediate this risk. Proteasomes are responsible for removing Oxidized Proteins and other Proteins that the cell has marked as “damaged” or Dysfunctional. Rlevels of damaged proteins within the heart correlately inverse with age as researches in rats shows.
FOXO Proteins mediate Autophagy and Proteasome activity. Increases in FOXO4 levels lead to increases in Proteasome activity and, thus, decreased levels of Oxidation and protein damage within a specific tissue. It may be possible that FOXO4-DRI or a variant of it can boost the heart’s natural Housekeeping functions and thus reduce Age-related changes in Cardiovascular function.
Neurodegenerative Disease
Age-related changes in cognitive function have a complex Etiology.The medical community still doesn’t fully understand Alzheimer’s and other common diseases. There is some evidence, that support the notion changes in Proteasome activity can lead to or Exacerbate underlying Neurodegenerative conditions. It is unclear if impaired Proteasome activity is a primary cause or secondary contributor to diseases like Alzheimer’s. However, impairment of the systems has been found in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and Prion disease. There is also impairment of Proteasome function in Amyotrophic lateral Sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease).
The Central Nervous System have FOXO Proteins modified in, researchers found that FOXO Protien may help treating or prevening Neurodegnerative Disorders. At the very least, there is hope that FOXO4-DRI and other modified FOXO Proteins may help slow the Relentless Progression of Neurodegenerative Disorders.